前言
无意中浏览到了这样的一个 repo,叫《每周十道前端大厂面试题》(https://github.com/airuikun/Weekly-FE-Interview),看到里面其中的一些题目觉得挺有意思,就深度解答一下
第 7 题:手写代码,简单实现apply
// ES 6 版本
Function.prototype.apply2 = function(context, arr) {
let context = context || window; // 因为传进来的 context 有可能是 null
context.fn = this;
arr = arr || [];
const result = context.fn(...arr); // 相当于执行了 context.fn(arguments[1], arguments[2]);
delete context.fn;
return result; // 因为有可能 this 函数会有返回值 return
}第 8 题:手写代码,简单实现 bind
// ES 6 版本
Function.prototype.bind2 = function() {
var fn = this;
var argsParent = [...arguments];
return function() {
fn.call(...argsParent, ...arguments);
};
}第 10 题:简单手写实现 promise(这里深度实现)
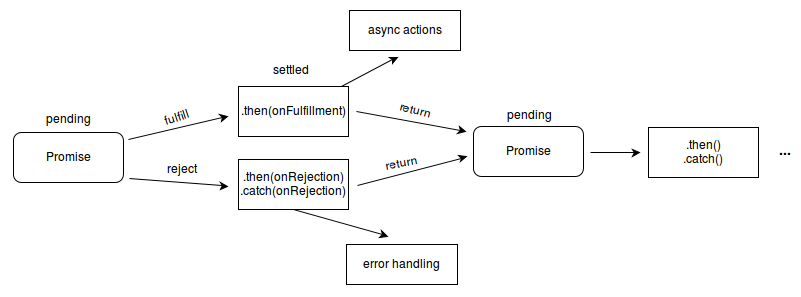
// 支持多层then链式调用(then中可返回新的promise进行异步流控制),支持catch及finally
function Promise2(fn) {
this.onFulfilledCb = null
this.onRejectedCb = null
this.onFinallyCb = null
this.onCatchCb = null
this.thenResultPromise = null
this.promiseValue = null
this.promiseStatus = 'pending' // pending, fulfilled, rejected
this.timer = null
var _this = this
var resolve = function(data) {
_this.promiseValue = data
try {
_this.onFulfilledCb &&
(_this.thenResultPromise = _this.onFulfilledCb(data))
} catch (e) {
_this.onCatchCb && _this.onCatchCb(e)
}
_this.onFinallyCb && _this.onFinallyCb()
_this.promiseStatus = 'fulfilled'
}
var reject = function(error) {
_this.promiseValue = error
try {
_this.onRejectedCb
? (_this.thenResultPromise = _this.onRejectedCb(error))
: _this.onCatchCb && _this.onCatchCb(error) // 不处理 reject 的数据会被 catch 到的
} catch (e) {
_this.onCatchCb && _this.onCatchCb(e)
}
_this.onFinallyCb && _this.onFinallyCb()
_this.promiseStatus = 'rejected'
}
if (typeof fn === 'function') {
// 异步回调串联
fn(resolve, reject)
} else {
resolve()
}
}
Promise2.prototype = {
then: function(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
var _this = this
onFulfilled && (_this.onFulfilledCb = onFulfilled)
onRejected && (_this.onRejectedCb = onRejected)
return new Promise2(function(resolve2, reject2) {
_this.timer = setInterval(function() {
// 使用轮循的方式检测 then 的两个参数函数返回的 promise 是否已经 fulfilled 或者 rejected
try {
if (
_this.promiseStatus !== 'pending' &&
_this.thenResultPromise.promiseStatus !== 'pending'
) {
if (_this.thenResultPromise.promiseStatus === 'fulfilled') {
resolve2(_this.thenResultPromise.promiseValue)
} else if (
_this.thenResultPromise.promiseStatus === 'rejected'
) {
reject2(_this.thenResultPromise.promiseValue)
}
_this.timer && clearInterval(_this.timer)
}
} catch (e) {
reject2(e)
_this.timer && clearInterval(_this.timer)
}
}, 10)
})
},
catch: function(onCatch) {
this.onCatchCb = onCatch
return this // 实现链式调用
},
finally: function(onFinally) {
this.onFinallyCb = onFinally
}
}
/****************** 测试数据 *******************/
var myPromise = new Promise2(function(resolve, reject) {
// 当异步代码执行成功时,我们才会调用 resolve(...), 当异步代码失败时就会调用 reject(...)
// 在本例中,我们使用 setTimeout(...) 来模拟异步代码,实际编码时可能是 XHR 请求或是 HTML5 的一些 API 方法.
console.log('----------------- 流程开始 --------------------')
setTimeout(function() {
resolve('promise初始化resolve成功!') // 代码正常执行!
}, 500)
})
myPromise
.then(function(successMessage) {
return new Promise2(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(
'myPromise then 1 收到 resolveMessage:' + successMessage
)
reject('from then 1')
}, 3000)
})
})
.then(
function(successMessage) {
return new Promise2(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(
'myPromise then 2 收到 resolveMessage:' + successMessage
)
resolve('from then 2')
}, 2000)
})
},
function(failMessage) {
return new Promise2(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(
'myPromise then 2 收到 rejectMessage:' + failMessage
)
resolve('from then 2')
}, 1000)
})
}
)
.then(function(successMessage) {
return new Promise2(function(resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(
'myPromise then 3 收到 resolveMessage:' + successMessage
)
reject('from then 3')
}, 1000)
})
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log('caught rejected data:')
console.log(error)
})
.finally(function() {
console.log('-----------全部处理完毕!-----------')
})第 14 题:简单实现 async / await 中的 async 函数
参考引用自:https://www.jb51.net/article/140002.htm
// async 函数的实现,就是将 Generator 函数和自动执行器,包装在一个函数里。
/*
async function fn(args) {
// ...
}
// 等同于
function fn(args) {
return spawn(function* () {
// ...
});
}
*/
// 所有的 async 函数都可以写成上面的第二种形式,其中的 spawn 函数就是自动执行器。
// 下面给出 spawn 函数的实现,基本就是前文自动执行器的翻版。
function spawn (genF) {
// var count = 0 // 用于统计yield的个数,相当于await的个数
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
var gen = genF()
function step (nextF) {
// count++
try {
var next = nextF()
} catch (e) {
return reject(e)
}
if (next.done) {
// console.log(count - 1) // 输出被执行的异步函数的个数,即yield的个数
return resolve(next.value)
}
Promise.resolve(next.value).then(function (v) {
step(function () {
return gen.next(v)
})
}, function (e) {
step(function () {
return gen.throw(e)
})
})
}
step(function () {
return gen.next(undefined)
})
});
}
function fn (args) { // 验证结果
return spawn(function* () {
var a = yield (new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('a完成了!')
}, 3000)
}))
console.log('A: ', a)
var b = yield (new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(a + ' | b也完成了!')
}, 3000)
}))
console.log('B: ', b)
})
}
fn() // 开始执行,验证结果第 4 题:如何遍历一个 dom 树
Node Types
文档、元素、属性以及 HTML 或 XML 文档的其他方面拥有不同的节点类型。
存在 12 种不同的节点类型,其中可能会有不同节点类型的子节点:
| 节点类型 | 描述 | 子节点 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Element | 代表元素 | Element, Text, Comment, ProcessingInstruction, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| 2 | Attr | 代表属性 | Text, EntityReference |
| 3 | Text | 代表元素或属性中的文本内容。 | None |
| 4 | CDATASection | 代表文档中的 CDATA 部分(不会由解析器解析的文本)。 | None |
| 5 | EntityReference | 代表实体引用。 | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| 6 | Entity | 代表实体。 | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| 7 | ProcessingInstruction | 代表处理指令。 | None |
| 8 | Comment | 代表注释。 | None |
| 9 | Document | 代表整个文档(DOM 树的根节点)。 | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, DocumentType |
| 10 | DocumentType | 向为文档定义的实体提供接口 | None |
| 11 | DocumentFragment | 代表轻量级的 Document 对象,能够容纳文档的某个部分 | Element, ProcessingInstruction, Comment, Text, CDATASection, EntityReference |
| 12 | Notation | 代表 DTD 中声明的符号。 | None |
代码如下:
function traversal(node) {
// 对node的处理
if (node) {
console.log('[')
console.log('-- Node Type: ' + node.nodeType)
console.log('-- Tag Name: ' + node.tagName)
console.log(node)
console.log(']')
}
var i = 0,
childNodes = node.childNodes,
item
for (; i < childNodes.length; i++) {
item = childNodes[i]
if (item) {
// 递归先序遍历子节点
traversal(item)
}
}
}请写一个正则,去除掉 html 标签字符串里的所有属性,并保留 src 和 href 两种属性
const nonSrcHrefAttribute = /\s(?!href=|src=)[^\s"'<>/=]+(?:\s*(=)\s*(?:"([^"])"+|'([^'])'+|([^\s"'=<>`]+)))?/g解释一下在 js 里,0.1+0.2 为什么等于 0.30000000000000004,如何通过代码解决这个问题?
function add() {
var args = [...arguments]
var maxLen = Math.max.apply(
null,
args.map(item => {
var str = String(item).split('.')[1]
return str ? str.length : 0
})
)
return args.reduce((sum, cur) => sum + cur * 10 ** maxLen, 0) / 10 ** maxLen
}
console.log(add(0.1, 0.2)) // => 0.3
console.log(add(10, 11)) // => 21
console.log(add(0.001, 0.003)) // => 0.004
对你的第十题的then 函数做了如下改动,感觉是可以不用轮询的
是吗?测试过没有,我找时间测试一下